Projects
Ongoing Projects
Role as PI/Co-PI
Developing AI-driven Safe Navigation Tool.

There is a need for a real-time navigation system that can provide data-driven decision on the safest path or route. Conducting safety prediction by using big data, and AI-driven algorithms perform better than conventional statistical models. This study aims to conduct a unique contribution by developing a robust, AI-driven, safe navigation tool, which can provide an informed decision of the safest route.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $330,000. Year: 2021-2023.

Develop a Real-Time Decision Support Tool for Urban Roadway Safety Improvements.
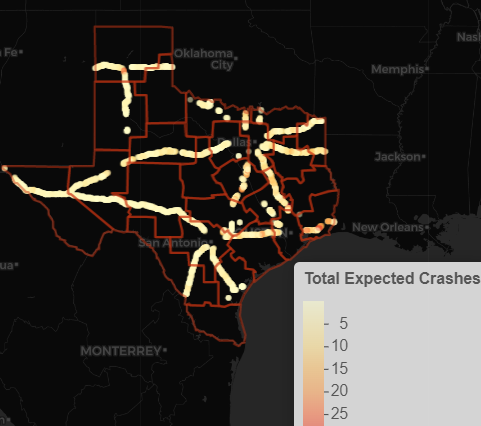
This study used three national databases [National Performance Management Research Data Set (NPMRDS), Travel Monitoring Analysis System (TMAS), and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)] to develop SPFs (both annual and short-duration) for urban roadways.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $470,000. Year: 2022-2024.

Using Vehicle Probe Data to Evaluate Speed Limits on Texas Highways.
The objective of this research is to determine whether speed probe data can be used rather than the current approach for collecting speed data. This study will explore data availability and relative costs for conducting a region-wide speed zoning study.
Co-PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $400,000. Year: 2022-2024.

Leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) Techniques to Detect, Forecast, and Manage Freeway Congestion.
This project envisions to mitigate the current research gap by conducting two major project phases. The first phase can confirm the validity of commercial data sources for planning and operations, while the second involves understanding which AI models/ algorithm are the most suitable for addressing TxDOT needs based on desirable use cases and data availability.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $310,000. Year: 2021-2023.

Safety Enhancements at Short-Storage-Space Railroad Crossings.
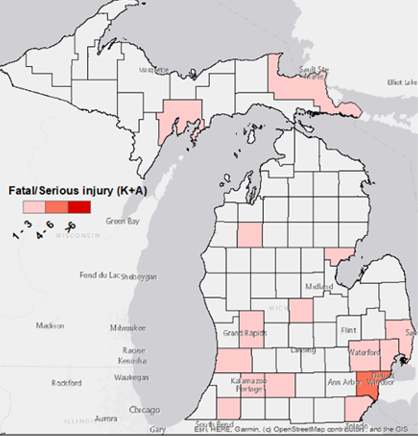
Michigan Department of Transportation (MDOT) estimates there are at least 300 crossings that have these conditions throughout the state, including but not limited to, crossings along the CSX corridor that parallels Chicago Drive from Hudsonville to Zeeland. This study will explore the scopes for safety enhancements at short-storage space rail crossings in Michigan.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $110,000. Year: 2019-2023.

Develop Speed Crash Modification Factors (CMFs) from SHRP-2 Data.
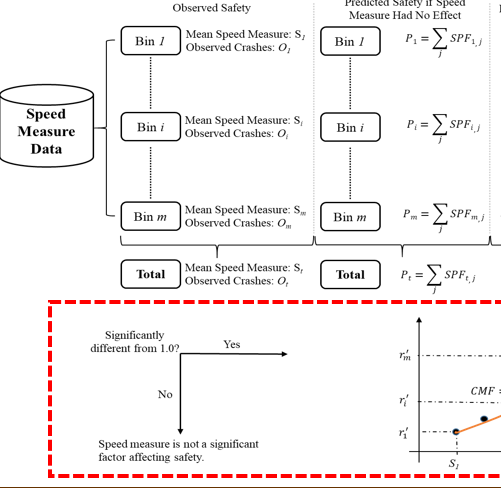
This study will develop speed CMFs for both rural and uran faciltiies. This study will use both NPMRDS and SHRP-2 RID data to develop segment level information with incorporation of operating speed measures. The speed SPFs will address the issue of ommiting variable efffect by making the models more robust.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $189,891. Year: 2019-2023.

Role as Key Researcher
NCHRP 15-76: Designing for Target Speed

The American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) defines design speed as “a selected speed used to determine the various geometric features of the roadway. The objectives of this research are to (1) determine the effects of roadway, roadside, and non-roadway elements on operating speeds on roadways with a target speed between 30 and 40 mph and (2) develop recommendations on how the findings can be incorporated into the roadway design process.
Year: 2022-2024.

NCHRP 07-30: Methods for Assigning Short-Duration Traffic Volume Counts to Adjustment Factor Groups for Estimating AADT
Annual average daily traffic (AADT) which represents traffic on a typical day of the year is used by transportation agencies for reporting requirements, allocating resources, informing decision-making, and supporting various agency functions. The objective of this research is to develop rational methods for assigning short-duration traffic volume counts to adjustment factor groups for estimating AADT. The research is concerned with all functional classes of roadways and traffic volumes.
Year: 2022-2024.

NCHRP 03-144: Leveraging Existing Traffic Signal Assets to Obtain Quality Traffic Counts and Enhance Transportation Monitoring Programs

The objectives of this research are to (a) determine the feasibility of using existing or enhanced traffic equipment to collect, store, and disseminate data for purposes other than traffic operations, particularly for traffic monitoring programs; (b) determine the suitability of traffic count data from already installed and existing traffic assets for this purpose; and (c) develop effective practices for obtaining and integrating traffic counts from existing traffic assets.
Year: 2022-2024.

Using Machine Leaning Tools to Identify Pedestrian Crash Types.
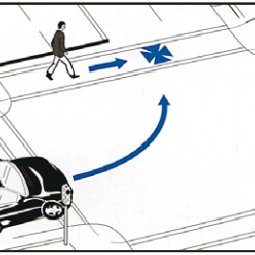
This study collected crash narrative data from three cities in Texas. Pedestrian related crash data have been collected for the recent three years. This study applied natural language processing to classify pedestrin crash typing by following the protocol designed by PBCAT 3.0.
Year: 2022.

NCHRP 17-71A: Proposed AASHTO Highway Safety Manual, Second Edition.

The objective of this research is to complete the work begun in NCHRP Project 17-71 to develop and prepare a proposed HSM2 in a format suitable for adoption as an AASHTO publication. The proposed HSM2 will synthesize and incorporate relevant ongoing and completed research including finished NCHRP Project 17-71 deliverables, related documents, and user feedback in order to expand the scope and quality of HSM2 to increase application and improve its usability.
Year: 2021-2022.

Develop Highway Safety Manual (HSM) Safety Performance Functions (SPFs) and Calibration Factors for Texas

The research team will develop Texas-specific SPFs and calibration factors for various facility types, including freeways and interchanges per HSM recommendations. Depending upon the data analysis, separate calibration factors may need to be developed for each region (North, South, East & West).
Year: 2021-2022.

Enhancing Freeway Safety Prediction Models.

This research project will develop new safety prediction models for 12-lane freeway segments and segments with managed lanes, and also derive local calibration factors for models for urban freeway segments. The project will also develop an analysis tool to help practitioners implement the new models to facilitate analysis of complex urban freeway configurations.
Year: 2019-2022.

Improving and Communicating Speed Management Practices.

This research is designed to increase the profession’s understanding of the fundamental relationships between posted and operating speed, develop consistent procedures for the establishment of posted speed limits and the use of technologies to increase driver awareness, and provide content to support external and internal TxDOT dialog about speed limits.
Year: 2019-2022.

NCHRP 03-134: Determination of Encroachment Conditions in Work Zones

The objective of this research is to evaluate work zone encroachments and develop guidance to improve safety for workers and the traveling public in roadway work zones. The guidance should address all aspects of work zones from planning through implementation, and be useable by any entity involved in the life cycle of the work zone.
Year: 2019-2022.

NCHRP 17-92: Developing Safety Performance Functions for Rural Two-Lane Highways that Incorporate Speed Measures.

The objective of this research is to develop a predictive methodology for rural two-lane, two-way highways, for consideration by the AASHTO HSM Steering Committee, that incorporates speed measures (or surrogates for speed measures) to estimate crash frequency and severity.
Year: 2019-2024.

NCHRP 14-41: Permanent Vegetation Control Treatments for Roadsides.

The objective of this research is to produce up-to-date guidance for transportation agencies for selecting appropriate permanent vegetation controls that will be effective in preventing or significantly retarding the growth of unwanted vegetation around roadside appurtenances and along roadsides.
Year: 2018-2022.

Completed Projects
Role as PI/Co-PI
Autonomous Delivery Vehicle as a Disruptive Technology: How to Shape the Future with a Focus on Safety?
This research involves conducting a review of the literature; gathering and integrating several datasets such as aggregated ADV trips and trajectories, ADV incidents, demographic data, crash, roadway, and traffic data, and crowdsourced data from multiple sources.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $2,300,000. Year: 2020-2022.

Use of Disruptive Technologies to Support Safety Analysis and Meet New Federal Requirements
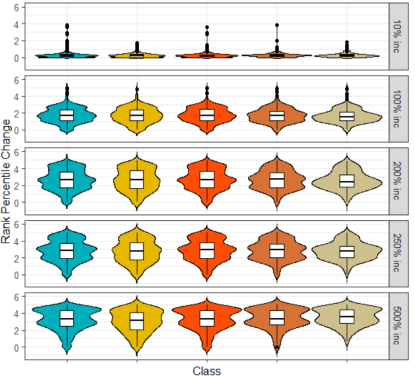
The goal of this project was to determine the accuracy of AADT estimates developed from alternative data sources and quantify the impact of AADT on safety analysis. The sensitivity analysis revealed that the impact of AADT on safety analysis mainly depends on the size of the network, the AADT coefficients, and the overdispersion parameter of the SPFs.
Co-PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $1,601,000 Year: 2019-2021.

Develop a Real-Time Decision Support Tool for Rural Roadway Safety Improvements.

Conventional crash risk analysis typically omits real-time speed, real-time volume, and weather data, significantly limiting safety predictive methods. To mitigate this research gap, this study used three national databases (NPMRDS, TMAS, and NOAA) to develop SPFs for rural roadways.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $300,000. Year: 2019-2021.

Exploring Crowdsourced Monitoring Data for Safety
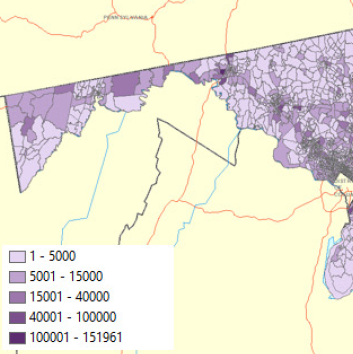
In the recent years, there is an enormous growth of probe based data companies as well as companies that collect information from smart and connected vehicles. This project included four distinct but related exploratory studies of data sources that could improve roadway safety analysis.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $20,000. Year: 2019.

NCHRP 20-07 (Task 384): Core Competencies for Key Safety Training
The objectives of this project were to: (1) Compile a research synthesis on education and training opportunities related to key safety analysis; (2) Develop a user-friendly tool for states to assess their workforce development needs; and (3) Provide a useable template for highway agencies to identify effective and efficient training and education opportunities.
Co-PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $75,000 Year: 2018-2019. Status: Completed.

Transportation Safety Planning Noteworthy Practices
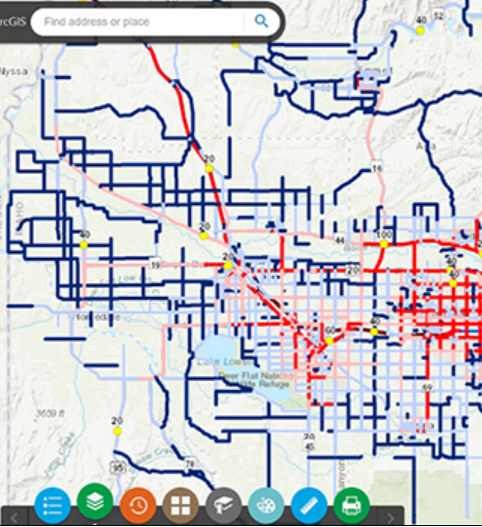
ransportation Safety Planning (TSP) is a comprehensive, system-wide, multimodal, proactive process that better integrates safety into surface transportation decision-making. Federal law requires that the State and Metropolitan transportation planning processes be consistent with Strategic Highway Safety Plans.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $30,000 Year: 2018-2019. Status: Completed.

Rural Speed Safety Project for USDOT Safety Data Initiative.

The objective of this project was to examine prevailing operating speeds on a large scale to determine how speed and speed differentials interact with roadway characteristics to influence the likelihood of crashes. The overall finding was that speed-related operational information is an area of opportunity to better understand safety outcomes.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $240,000 Year: 2018-2019. Status: Completed.

NCHRP 14-40: Comparison of Cost, Safety, and Environmental Benefits of Routine Mowing and Managed Succession of Roadside Vegetation.
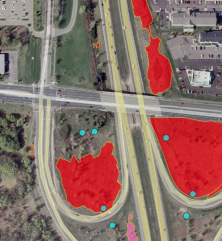
The objective of this project was to examine prevailing operating speeds on a large scale to determine how speed and speed differentials interact with roadway characteristics to influence the likelihood of crashes. The overall finding was that speed-related operational information is an area of opportunity to better understand safety outcomes.
Co-PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $300,000 Year: 2017-2019. Status: Completed.

TCRP Synthesis SB-33: Uses of Social Media in Public Transportation
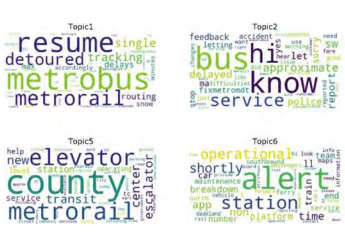
A literature review and completed survey responses of social media practices of 46 transit agencies were collected. An analysis on the state of the practice, emphasizing lessons learned, current practices, challenges, and gaps in information is provided.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $45,000 Year: 2020-2021. Status: Completed.

Louisiana’s Alcohol-Impaired Driving Problem: An Analysis of Crash and Cultural Factors
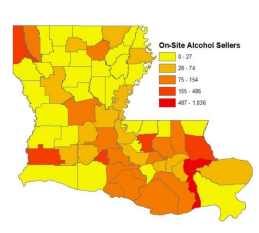
A review of the literature identified cultural groups and how those different groups approach age of first consumption, consistent alcohol usage, and binge drinking. Key findings include the need to recognize culture as a critical factor, acknowledge the problem as statewide, provide diverse transportation options, and recognize the critical role of education and outreach.
CO-PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $175,000 Year: 2020-2021. Status: Completed.

Safety Impacts of Reduced Visibility in Inclement Weather
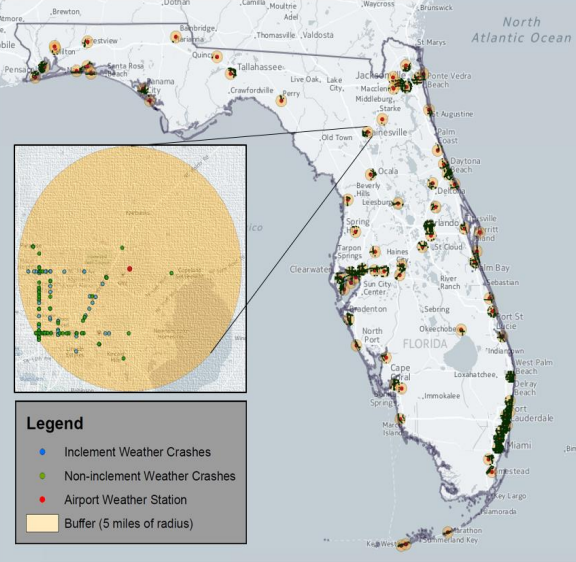
This research seeks to better understand the ramifications of inclement weather on safety from a perspective of visibility. The findings indicate that the likelihood of a crash increases during periods of low visibility, despite the tendency for less traffic and lower speeds to prevail during these times.
PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $44,000 Year: 2016.

Urban Roadway Fatality Analysis.
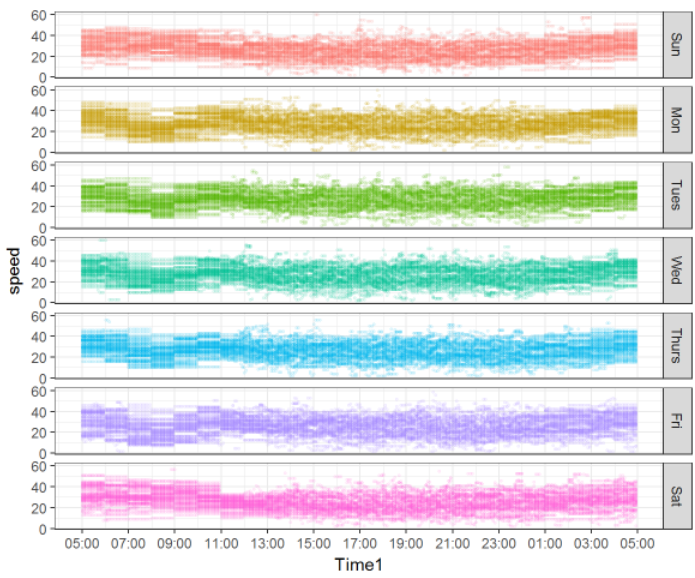
This projects examines the impact of speed on urban roadway fatalities. Using data from Inrix, this studty developed databases by determining different speed measures. This study has deveoped several reproducible workflows in exploring bug data from Inrix. Finally, urban roadway related fatalities were explored.
Co-PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $30,000 Year: 2016. Status: Completed.

User Sentiment Analysis with Louisiana Social Media Data for Better and Effective Crash Countermeasures.
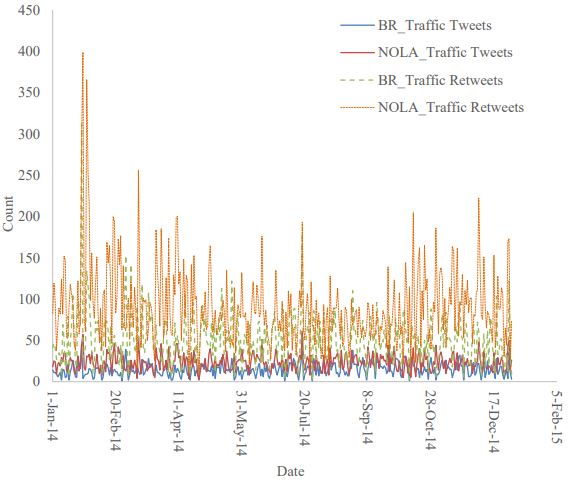
This project examines the promising aspects of the governmental transportation authorities in providing information to the people. Researchers perform semantic analysis on the tidy dataset to extract knowledge. This study demonstrates how text mining retrieves knowledge from official transportation information tweets.
Co-PI: Subasish Das. Budget: $30,000 Year: 2015. Status: Completed.

Role as Key Researcher
NCHRP 17-66: Guidance for Selection of Appropriate Countermeasures for Opposite Direction Crashes

NCHRP Research Report 995: Guidelines for Treatments to Mitigate Opposite Direction Crashes provides state departments of transportation (DOTs) practitioners and other transportation professionals with comprehensive guidelines for the selection of cost effective countermeasures to address opposite direction crashes.
Budget: $300,000. Year: 2017-2021. Status: Completed.

Development of Pedestrian Intersection Crash Modification Factors.
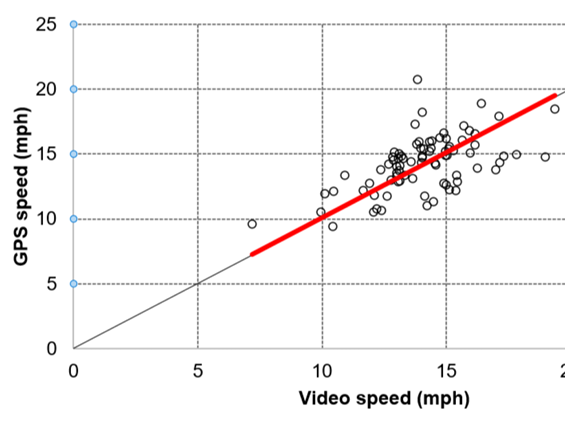
This project investigated the influence of intersection corner radius on pedestrian crashes and right-turn vehicle speed. The corner radius can be unique to each corner at an intersection; therefore, this study assigned crashes to an intersection corner rather than to the entire intersection.
Year: 2019-2021.

NCHRP 06-18: Guide for Snow and Ice Control Operations.
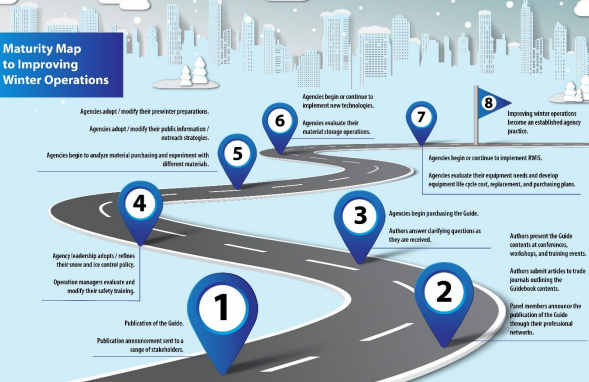
The objective of this research was to develop a guide that will serve as the primary source for guidance on all aspects of snow and ice control operations. The guide was intended for adoption/publication by AASHTO and will supersede the 1999 AASHTO Guide for Snow and Ice Control, and other guidance on snow and ice control operations.
Year: 2019-2022.

Collection and Estimation of Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT) on Lower-Volume Roads.

This is an Informational Guide on traffic data collection and estimation of annual average daily traffic (AADT) for nonFederal aid-system (NFAS) roads. NFAS roads refer to rural minor collectors (6R) and both rural and urban local roads (7R and 7U).
Year: 2017-2019. Status: Completed.

NCHRP 17-76: Posted Speed Limit Setting Procedure and Tool: User Guide
NCHRP Research Report 966: This report provides a procedure for setting speed limits and a practitioner-ready user manual explaining the speed limit setting procedure (SLS-Procedure). Additionally, it provides an automated version of the SLS-Procedure via a spreadsheet-based Speed Limit Setting Tool (SLS-Tool).
Year: 2016-2018. Status: Completed.

Crash Modification Factor for Corner Radius, Right-Turn Speed, and Prediction of Pedestrian Crashes at Signalized Intersections

This project investigated the influence of intersection corner radius on pedestrian crashes and right-turn vehicle speed. The findings from the study support the development of a crash modification factor (CMF) for corner radius. The final selected model from this study can be used to predict turning speeds at different percentile levels.
Year: 2019-2021. Status: Completed.

Examine Trade-Offs Between Center Separation and Shoulder Width Allotment for a Given Roadway Width
The goal of this study is to advance HSIP evaluation processes and practices at the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) and evaluate the safety and cost effectiveness of Highway Safety Improvement Program (HSIP) projects and countermeasures or work codes (WCs) that have been implemented in Texas over the last few years.
Year: 2019-2021. Status: Completed.

Evaluation of Roadside Treatments to Mitigate Roadway Departure Crashes
This report presents findings from a research project that sought to provide a systemic framework to identify high-risk locations for roadway departure crashes and applicable countermeasures for implementation. The products of the project are intended to assist TxDOT districts with selecting projects that address roadway departure crashes proactively as opposed to reactively.
Year: 2018-2020. Status: Completed.

Evaluation of Highway Safety Improvement Projects and Countermeasures
The goal of this study is to advance HSIP evaluation processes and practices at the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) and evaluate the safety and cost effectiveness of Highway Safety Improvement Program (HSIP) projects and countermeasures or work codes (WCs) that have been implemented in Texas over the last few years.
Year: 2017-2019. Status: Completed.

Improving the Amount and Availability of Pedestrian and Bicyclist Count Data in Texas
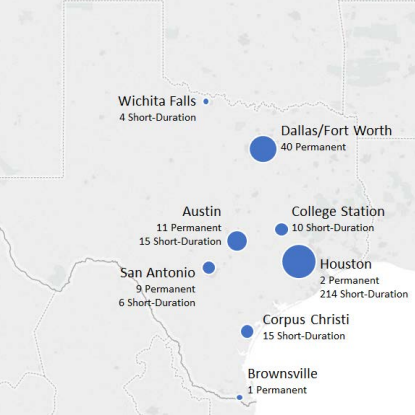
The first objective of this project was to recommend a count monitoring process for pedestrians and bicyclists that can be sustained statewide. The second objective was to develop a consolidated database of pedestrian and bicyclist counts from two pilot cities, as well as readily available pedestrian and bicyclist count data from other locations.
Year: 2017-2019. Status: Completed.

Vehicle Operating Speed on Urban Arterial Roadways

This research explored (1) the relationship between suburban vehicle operating speed and roadway characteristics, especially the presence of bicyclists and (2) whether crowdsourced speed data could be used to estimate the unconstrained speed for a location.
Budget: $286,773 Year: 2017-2018. Status: Completed.

Guide for Seasonal Adjustment and Crowdsourced Data Scaling
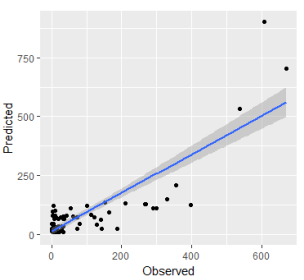
This guide describes a simple scaling process that estimates average annual daily bicyclists using the number of crowdsourced data samples, the functional class of the bicyclist travel facility, and the density of high-income households near the bicyclist travel facility.
Year: 2016-2018. Status: Completed.

Pavement Safety-Based Guidelines for Horizontal Curve Safety

In this research project, researchers calibrated detailed safety prediction models to account for the effects of key curve characteristics, including geometry, pavement variables (particularly skid resistance), and weather patterns. Additionally, researchers developed estimates of the service life for various surface treatments that may be used to increase skid resistance.
Year: 2016-2018. Status: Completed.

Guide for Scalable Risk Assessment Methods for Pedestrians and Bicyclists
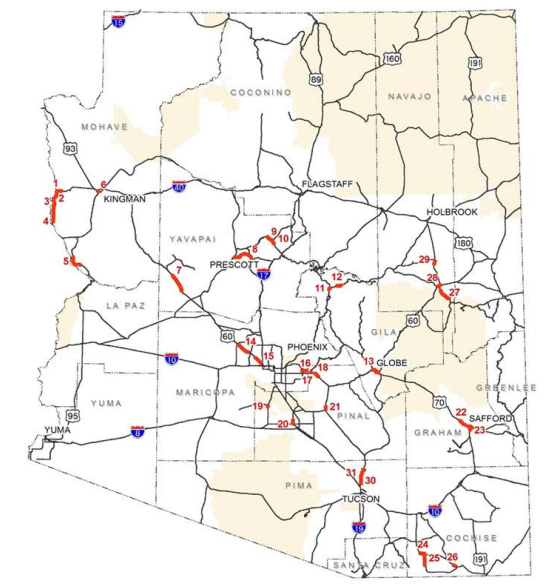
This guide describes scalable risk assessment methods for pedestrians and bicyclists, wherein risk is a measure of the probability of a crash to occur given exposure to potential crash events. This guide outlines eight sequential steps to develop risk values at various desired geographic scales, and describes the scope and nature of each step.
Year: 2016-2018. Status: Completed.

Analysis of the Shoulder Widening Need on the State Highway System
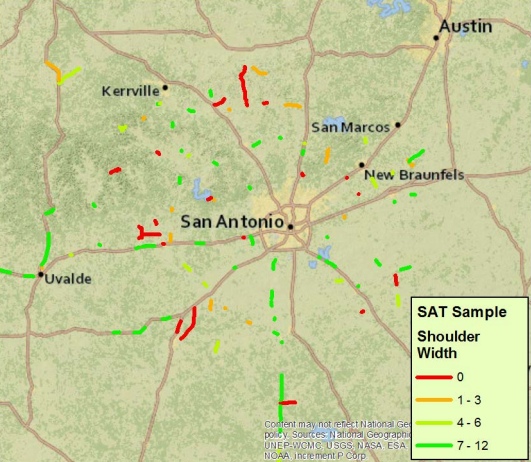
The overall objective of this project was to define the criteria for roadway shoulder suitability for pedestrians and bicycles, apply these criteria to Texas highways to determine candidate locations, identify high use or high demand locations, and develop a candidate list of potential target locations, to be incorporated into a Strategic Corridor Development Plan.
Year: 2014-2016. Status: Completed.

Synthesis of Methods for Estimating Pedestrian and Bicyclist Exposure to Risk at Areawide Levels and on Specific Transportation Facilities
This report summarizes the variety of methods used to estimate and evaluate exposure to risk in pedestrian and bicyclist safety analyses. In the literature, the most common definition of risk was a measure of the probability of a crash to occur given exposure to potential crash events.
Year: 2015-2017. Status: Completed.

Traffic Safety Improvements at Low Water Crossings

The objectives of this research project are: Investigate each TxDOT Area Office's current inventory and management approach of low water crossings. Survey other state DOTs, AASHTO, FHWA, and other agencies on low water crossing management techniques.
Year: 2018-2021. Status: Completed.

Identifying Infrastructure-Based Motorcycle Crash Countermeasures – Phase I.
To date, efforts to address motorcycle crashes have largely focused on driver-behavior issues. Infrastructure-based motorcycle-crash countermeasures can significantly improve motorcycle-rider safety; however, identifying effective countermeasures can be challenging.
Year: 2017-2019. Status: Completed.

Knowledge Extraction using Natural Language Processing from Farm Equipment related Crash Narratives.

This study collected traffic crash narrative data from different states. The narrative data are limited to farm equipment related collisions. Different machine learning models were applied on the crash narrative texts to identify the type of farm equipment. This study applied several natural language processing (NLP) tools to identify insights from the crash reports.
Year: 2017-2019. Status: Completed.

Measuring Automated Vehicle Safety.
This study conducted analysis on the safety criticial events associated with AV related crashes. The study was conducted for a private AV company and the analysis was done for the company so that they can make internal policy and design related modification.
Year: 2017. Status: Completed.

Field Evaluation of At-Grade Alternative Intersection Designs.
This is a multi-year project focusing on before-after data collection on alternative intersections. Alternative intersection data from several states have been collected during both before and after years and reports have been developed based on the data outcomes.
Year: 2016-2022.

Technical Support for Focus Approach to Roadway Departure (RwD) Safety.

Roadway departure (RwD) is a key concern on rural roadway safety. This study have developed safety implementation paln for roadway departure crashes for several states including Louisiana, West Virginia, Texas, and Arizona.
Year: 2016-2019. Status: Completed.

Safety Performance of Truck Lane Restrictions in Dallas-Fort Worth.

This study was undertaken to evaluate the safety performance of the truck lane restrictions (TLR) that have been implemented in the North Texas region. These truck lane restrictions prohibit semi- trucks (trucks) from using left-most freeway lane, or inner lane, except in passing or emergency maneuvers.
Year: 2016. Status: Completed.

Is Age a Factor in Crashes at Channelized Right-Turn Lanes? An Exploration of Potential Relationships

The objective of this research was to determine if a relationship exists between crashes and right-turn lane design characteristics with specific consideration of the age of the driver. The research team used crash data of selected intersections in Texas for a six-year period (2009�2014) to perform this study.
Year: 2015-2016. Status: Completed.

Developing a Method for Estimating AADT on all Louisiana Roads
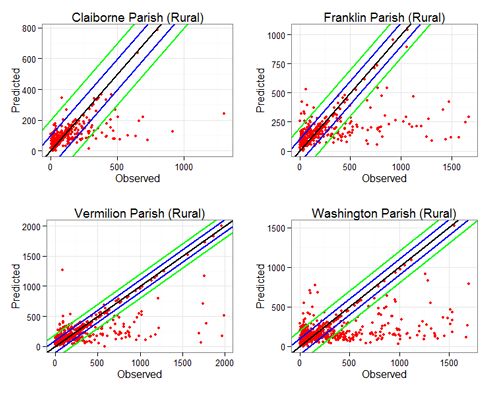
This study develops an annual average daily traffic (AADT) estimation methodology by using modern statistical and pattern recognition methods. By using available traffic counts on non-state roadway and four variables, a training set to estimate roadway AADT for eight parishes were obtained by a modified support vector regression method.
Year: 2013-2015. Status: Completed.

A Comprehensive Study on Pavement Edge Line Implementation
This project performed benefit and cost analysis. By considering the safety trend in Louisiana, the final estimated CMF is 0.85, which means there is a 15% expected crash reduction in edge line implementation on narrow, rural two-lane highways. The statistically estimated standard deviation for the CMF is 0.039.
Year: 2012-2014. Status: Completed.

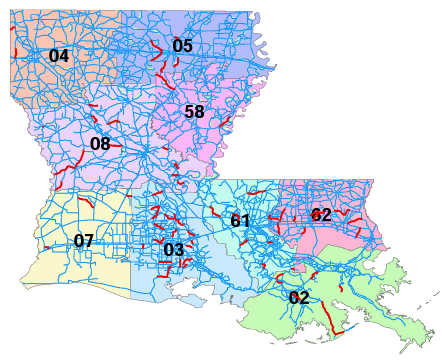
Developing Louisiana Crash Reduction Factors
After reviewing and documenting crash countermeasures as well as their crash modification factors (CMF), the research team developed two CMFs that are unique in Louisiana. The first CMF is for converting four-lane urban undivided roadway to five-lane roadway. The second CMF developed is for raised pavement markers and striping.
Year: 2011-2013. Status: Completed.

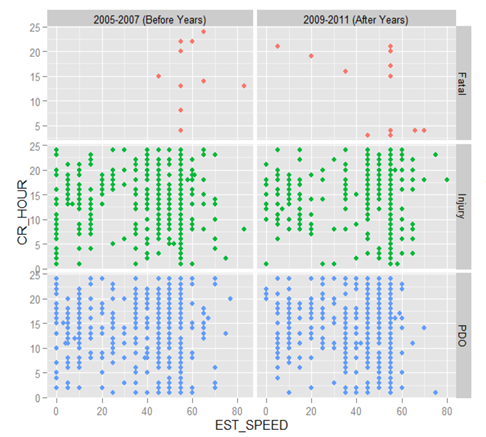
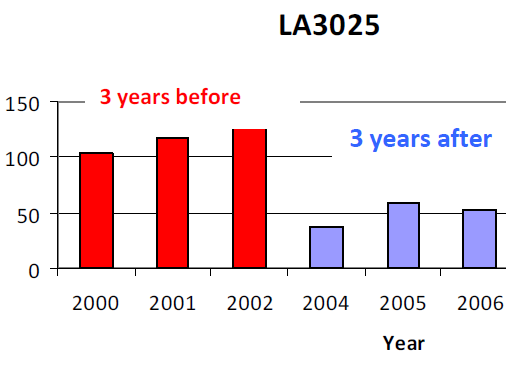
Safety Improvement from Edge Lines on Rural Two-Lane Highways
More than 40 percent of rural, two-lane highways in Louisiana has a pavement width less than 22 ft with no edge lines. This project investogated the safety impact of edge lines on these roadways by analyzing crash frequencies before and after edge line implementations on a group of selected narrow, rural two-lane highways from all LADOTD districts.
Year: 2010-2012. Status: Completed.
